Suppose the current Docker version is 18.09, and the target version for the upgrade is 20.10. There are several methods for upgrading, such as manual upgrading, utilizing convenience scripts, or leveraging the APT repository.
Upgrading Docker Using the APT Repository
1) Verify the latest Docker package version in the APT cache with the command: apt-cache policy docker-ce
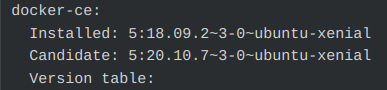
If the package is present, execute the following command,
apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.ioWhere, docker-ce is the primary Docker engine package for the community edition.docker-ce-cli, is optional but recommended to upgrade alongside the Docker engine package. It provides a Docker client that communicates with the Docker engine (dockerd daemon) through API calls.containerd.io, is also optional but advisable to upgrade alongside the Docker engine package. containerd is the service responsible for managing the complete lifecycle of a container on a host.
After completing the upgrade, execute ‘docker version.’ You should observe the latest Docker version (20.10.7) installed.
Example output
Client:
Version: 20.10.7
API version: 1.39
Server: Docker Engine - Community
Engine:
Version: 20.10.7
API version: 1.41 (minimum version 1.12)
containerd:
Version: 1.4.6
GitCommit: d71fcd7d8303cbf684402823e425e9dd2e99285d
In case the latest Docker package version (20.10) is not found in the APT cache, you need to initially add the Docker APT repository and perform an ‘apt-get update.’ Afterward, you can proceed to upgrade the Docker version to the latest using the following command:apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
docker APT repository information found here,
https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/#install-docker-engine
What is the impact of upgrading Docker on already running containers?
NOTE: Prior to the Docker upgrade, the Docker daemon is automatically stopped, thereby halting all running Docker containers. After the upgrade, the Docker daemon restarts automatically, but it does not resume the stopped containers.
Suppose your application, running on Docker containers, is sensitive and requires zero downtime. In such cases, careful planning and maintenance are necessary during the Docker upgrade.
However, if a brief period of container downtime is acceptable (depending on the application’s ability to quickly start and resume traffic), there is an option called
restart: unless-stoppedWhen this option is added to each section of the Docker containers in the docker-compose.yml file, the Docker containers that automatically stop just before the Docker upgrade will be automatically restarted after the upgrade. This automated process eliminates the need to start each Docker container manually, minimizing downtime for the applications.
The restart: unless-stopped option essentially means that the container will always be restarted (even after the Docker daemon restarts) if it stops, except in the case when the container is manually stopped by a user.




